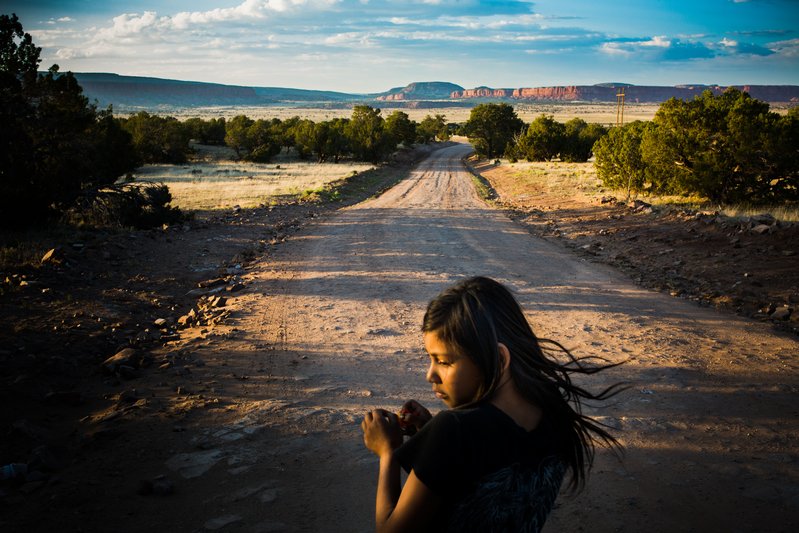
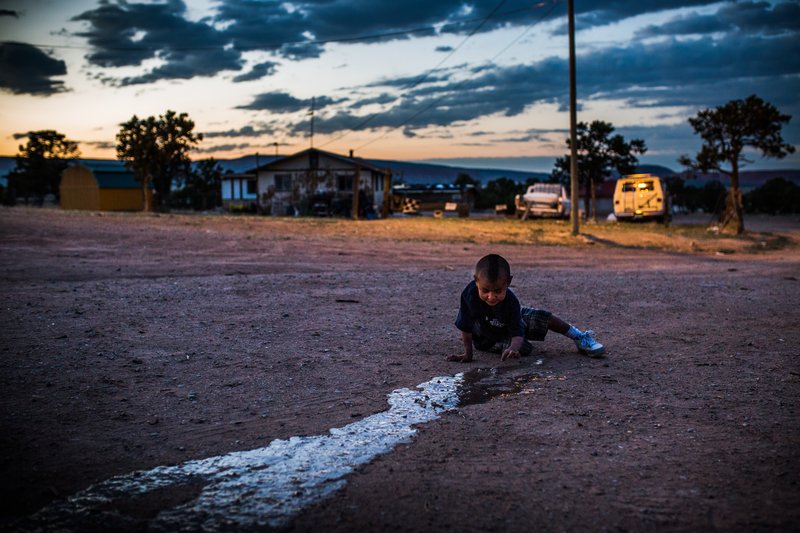
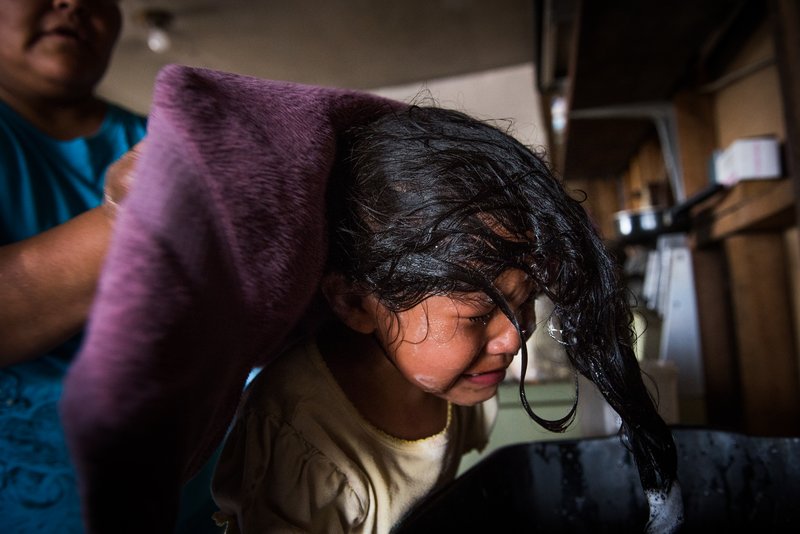
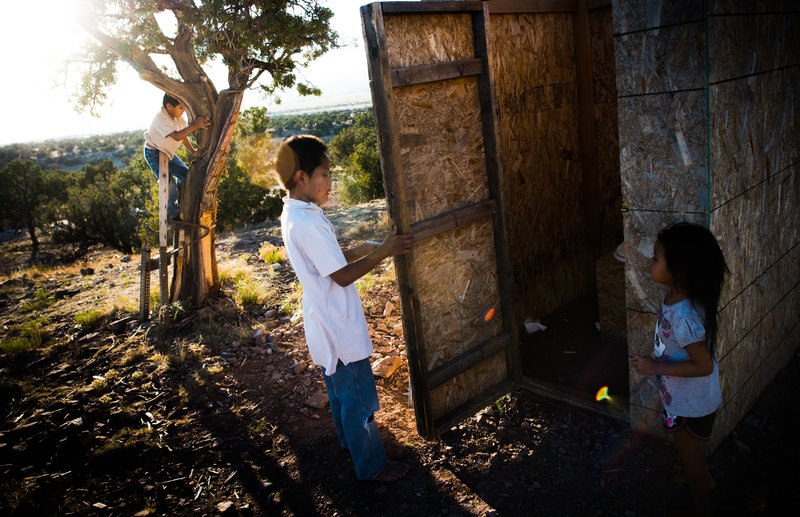
CPOY 72 Documentary Award of Excellence: On Poisoned Land
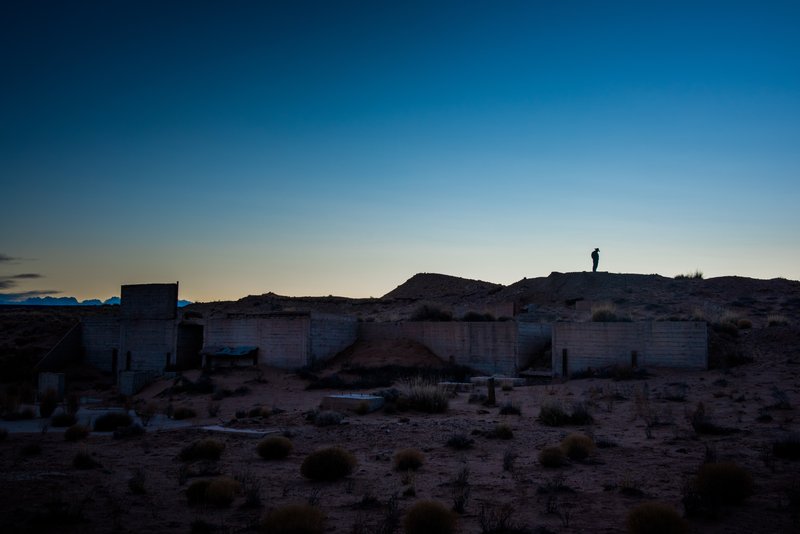
On July 16, 1945, the first atomic bomb detonation took place in a test explosion near Socorro, New Mexico, setting into motion an arms race that needed one main raw ingredient: weapons-grade uranium. Land in the American Southwest that was made up of barren desert scrub brush and sandstone mesas was found to be incredibly rich in uranium ore. The people of the Navajo Nation sat on some of the largest uranium deposits in the world. Hundreds of mines were opened and a boom began. But as is so often the case with indigenous populations, the vast majority of Navajos did not benefit from their own natural resources and unemployment now rests above 40 percent. Decades of irresponsible mining, chemical dumping, and radioactive spills have left large swathes of the Navajo Nation with crystal clear, yet contaminated and undrinkable ground water.
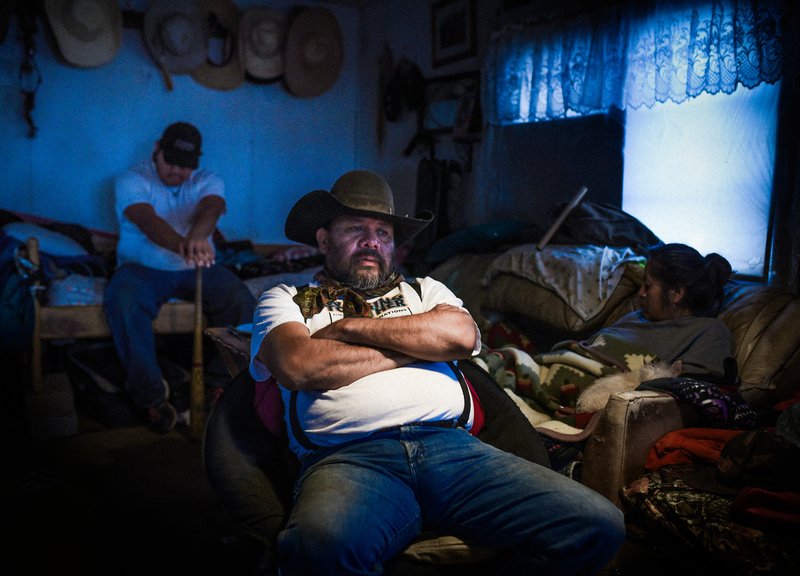
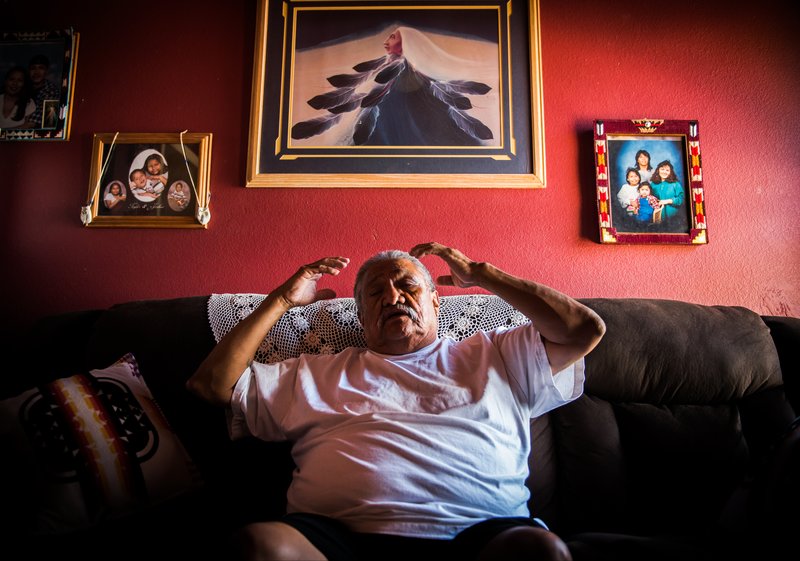
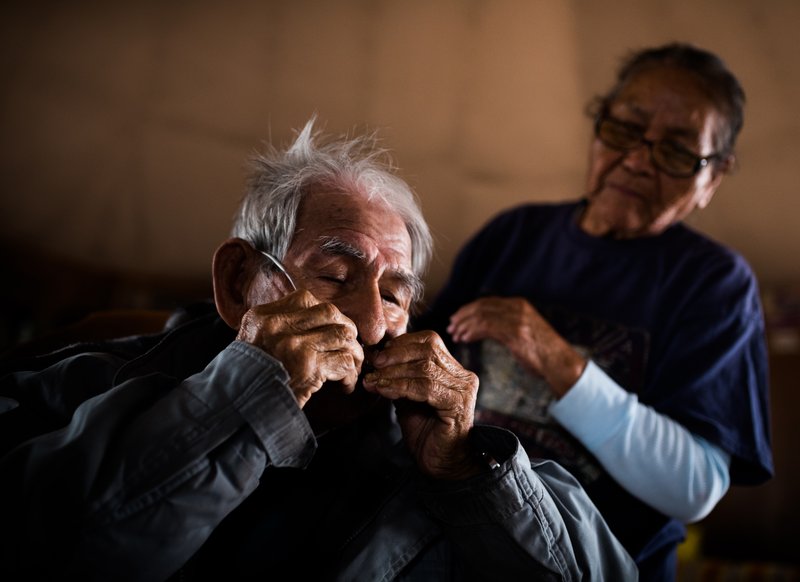
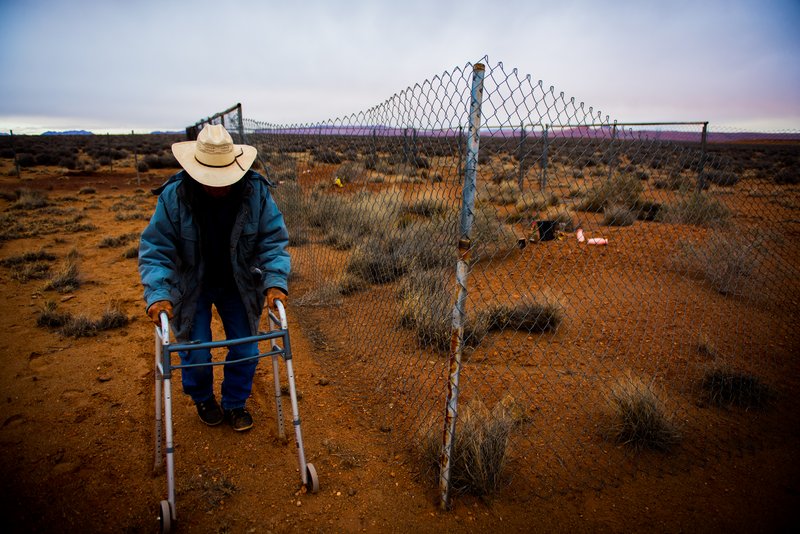
More than a decade has passed since the last uranium was mined on Navajo land, but the death and disease it brought is far less removed. Over 30,000 sick Navajo miners have been compensated under the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act that awards a cash sum to those who can prove that they are sick or dying from their time spent working in the mines. Many more will die in the coming years, but their legacy is lost on much of the country. The president has called for a second nuclear arms race as miners still die from the first.
In Navajo tradition, four sacred mountains are said to mark the edges of the Navajo’s land and are believed to watch over the people. In one prayer, the four mountains speak to the Navajo saying:
“My child I will feed you, give you good health, and I will give you strength and courage. My child I will give you clean air and clean water to drink. I am your Life.”
But from beneath the mountains on the Navajo Nation Reservation have come some of the richest deposits of uranium in the world, and with them sickness, suffering, pain, and loss. Today, the Navajo know this bitter irony all too well. They live it.